what are sources of biomass energy
August 26, 2024
Published
February 20, 2023
Top 10 countries interested in biomass energy
An Introduction to Biomass Energy
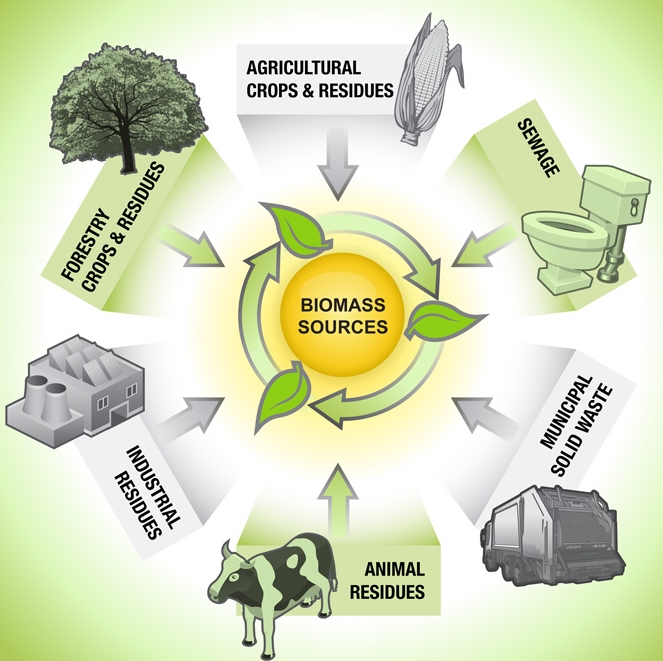 6. What are the advantages of biomass energy? The advantages of biomass energy include: - Renewable and sustainable: Biomass is derived from organic materials that can be replenished through natural processes, making it a renewable source of energy. - Reduction of greenhouse gas emissions: Biomass energy releases carbon dioxide during combustion, but this is offset by the carbon dioxide absorbed during the growth of biomass feedstocks. As a result, it has a significantly lower carbon footprint compared to fossil fuels. - Local resource utilization: Biomass energy reduces reliance on imported fossil fuels by utilizing locally available biomass resources, promoting energy security and supporting local economies. - Waste management: Biomass energy offers an environmentally friendly solution for managing agricultural residues, forest residues, and organic waste materials, reducing the need for landfilling and associated environmental impacts. - Potential for decentralized energy production: Biomass energy can be generated on a small scale, allowing for decentralized energy production and empowering communities to meet their energy needs locally. 7. What are the challenges associated with biomass energy? There are several challenges associated with biomass energy: - Resource availability: The availability of biomass resources varies depending on factors such as geographical location, climate, land use patterns, and competing uses (e.g., food production). Ensuring a sustainable and reliable supply of biomass feedstocks can be a challenge. - Technological limitations: Biomass energy technologies, such as combustion, gasification, and anaerobic digestion, require efficient and reliable conversion processes. Research and development are ongoing to improve the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of biomass energy technologies. - Environmental considerations: While biomass energy has environmental benefits, such as reduced greenhouse gas emissions, it is important to ensure that biomass cultivation and harvest practices are sustainable and do not lead to deforestation or habitat destruction. - Integration into existing energy systems: Integrating biomass energy into existing energy infrastructure, such as power grids, may require upgrades and modifications to accommodate the variable nature of biomass energy production. - Economic viability: The cost of biomass energy production and infrastructure can be a barrier to its widespread adoption. Government incentives, policy support, and economies of scale can help overcome economic challenges. 8. What are the different types of biomass energy technologies? There are several types of biomass energy technologies, including: - Combustion: This is the most common method, where biomass is burned to produce heat, which can be used for space heating, water heating, or electricity generation through steam turbines. - Gasification: Biomass is converted into a combustible gas mixture (syngas) through partial combustion in a controlled oxygen-deficient environment. The syngas can then be used to generate electricity or produce synthetic fuels. - Anaerobic digestion: Organic waste materials, such as agricultural residues and animal manure, are broken down by bacteria in an oxygen-free environment, producing biogas (composed mainly of methane) that can be used for electricity generation or as a heating fuel. - Pyrolysis: Biomass is heated in the absence of oxygen, leading to the formation of liquid bio-oil, gas, and a solid residue called biochar. The bio-oil can be used as a fuel or feedstock for the production of chemicals, while the biochar can be utilized as a soil amendment. 9. How does biomass energy contribute to the circular economy? Biomass energy plays a vital role in the circular economy by promoting resource efficiency and waste valorization. It helps close the loop by: - Utilizing organic waste materials and agricultural residues that would otherwise be discarded or left to decompose, thus reducing waste generation and associated environmental impacts. - Providing a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels by utilizing biomass feedstocks, which are derived from renewable resources. - Promoting the use of by-products and co-products from biomass energy production, such as ash, biochar, and biogas digestate, for beneficial applications in agriculture, construction, and industry. - Enabling the integration of biomass energy with other sectors of the circular economy, such as sustainable agriculture, forestry, and waste management. 10. How can individuals contribute to the development of biomass energy? Individuals can contribute to the development of biomass energy by: - Supporting policies and initiatives that promote the adoption of renewable energy, including biomass, at local, regional, and national levels. - Educating themselves and others about the benefits of biomass energy and its role in sustainable development and climate change mitigation. - Exploring opportunities for utilizing biomass fuels, such as wood pellets or biofuels, in residential heating systems or vehicles. - Participating in community-based initiatives or cooperatives that promote the use of biomass energy and support local biomass projects. - Advocating for investment in research and development of biomass energy technologies to improve efficiency and reduce costs. - Making sustainable choices in daily life, such as reducing energy consumption, recycling organic waste, and supporting sustainable land use practices. 11. What are the potential future developments in biomass energy? Future developments in biomass energy include: - Advanced conversion technologies: Ongoing research aims to improve the efficiency of biomass conversion processes, such as gasification and pyrolysis, to enhance energy yields and reduce environmental impacts. - Sustainable biomass production: Efforts are being made to develop sustainable biomass production systems that minimize land use conflicts, preserve biodiversity, and ensure the long-term availability of biomass feedstocks. - Integration with other renewable energy sources: Biomass energy can be integrated with other renewables, such as wind and solar power, to provide a more reliable and balanced energy supply. - Bioenergy with carbon capture and storage (BECCS): Biomass energy combined with carbon capture and storage technology has the potential to achieve negative emissions, effectively removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. - Biofuels for transportation: Advances in biomass energy research aim to develop more efficient biofuel production processes that can replace fossil fuels in the transportation sector. 12. How does biomass energy compare to other renewable energy sources? Biomass energy has several advantages and disadvantages compared to other renewable energy sources: Advantages: - Energy storage: Biomass can be stored and utilized on-demand, unlike solar and wind energy, which are intermittent. - Baseload power: Biomass power plants can provide continuous baseload power, similar to fossil fuel power plants. - Resource availability: Biomass feedstocks are readily available in many regions, offering a reliable and locally sourced energy option. - Carbon neutrality: Biomass energy is considered carbon-neutral because the carbon dioxide emitted during combustion is offset by the carbon dioxide absorbed during biomass growth. Disadvantages: - Land use: Biomass cultivation may require significant land resources, potentially leading to conflicts with food production or natural ecosystems. - Emissions and air quality: Biomass combustion can release air pollutants, such as particulate matter and volatile organic compounds, which may have adverse effects on air quality and human health if not properly managed. - Resource limitations: The availability of biomass resources is limited by factors such as land availability, climate conditions, and sustainable management practices. - Efficiency and cost: Biomass energy conversion technologies may have lower efficiencies and higher costs compared to more mature renewable energy technologies like solar and wind power. In conclusion, biomass energy offers a renewable and sustainable alternative to fossil fuels, contributing to reduced greenhouse gas emissions, improved waste management, and energy security. The top 10 countries interested in biomass energy have demonstrated significant commitment and success in its utilization. However, challenges persist and further advancements in technology, resource management, and policy support are essential to fully harness the potential of biomass energy in the transition towards a greener future.
6. What are the advantages of biomass energy? The advantages of biomass energy include: - Renewable and sustainable: Biomass is derived from organic materials that can be replenished through natural processes, making it a renewable source of energy. - Reduction of greenhouse gas emissions: Biomass energy releases carbon dioxide during combustion, but this is offset by the carbon dioxide absorbed during the growth of biomass feedstocks. As a result, it has a significantly lower carbon footprint compared to fossil fuels. - Local resource utilization: Biomass energy reduces reliance on imported fossil fuels by utilizing locally available biomass resources, promoting energy security and supporting local economies. - Waste management: Biomass energy offers an environmentally friendly solution for managing agricultural residues, forest residues, and organic waste materials, reducing the need for landfilling and associated environmental impacts. - Potential for decentralized energy production: Biomass energy can be generated on a small scale, allowing for decentralized energy production and empowering communities to meet their energy needs locally. 7. What are the challenges associated with biomass energy? There are several challenges associated with biomass energy: - Resource availability: The availability of biomass resources varies depending on factors such as geographical location, climate, land use patterns, and competing uses (e.g., food production). Ensuring a sustainable and reliable supply of biomass feedstocks can be a challenge. - Technological limitations: Biomass energy technologies, such as combustion, gasification, and anaerobic digestion, require efficient and reliable conversion processes. Research and development are ongoing to improve the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of biomass energy technologies. - Environmental considerations: While biomass energy has environmental benefits, such as reduced greenhouse gas emissions, it is important to ensure that biomass cultivation and harvest practices are sustainable and do not lead to deforestation or habitat destruction. - Integration into existing energy systems: Integrating biomass energy into existing energy infrastructure, such as power grids, may require upgrades and modifications to accommodate the variable nature of biomass energy production. - Economic viability: The cost of biomass energy production and infrastructure can be a barrier to its widespread adoption. Government incentives, policy support, and economies of scale can help overcome economic challenges. 8. What are the different types of biomass energy technologies? There are several types of biomass energy technologies, including: - Combustion: This is the most common method, where biomass is burned to produce heat, which can be used for space heating, water heating, or electricity generation through steam turbines. - Gasification: Biomass is converted into a combustible gas mixture (syngas) through partial combustion in a controlled oxygen-deficient environment. The syngas can then be used to generate electricity or produce synthetic fuels. - Anaerobic digestion: Organic waste materials, such as agricultural residues and animal manure, are broken down by bacteria in an oxygen-free environment, producing biogas (composed mainly of methane) that can be used for electricity generation or as a heating fuel. - Pyrolysis: Biomass is heated in the absence of oxygen, leading to the formation of liquid bio-oil, gas, and a solid residue called biochar. The bio-oil can be used as a fuel or feedstock for the production of chemicals, while the biochar can be utilized as a soil amendment. 9. How does biomass energy contribute to the circular economy? Biomass energy plays a vital role in the circular economy by promoting resource efficiency and waste valorization. It helps close the loop by: - Utilizing organic waste materials and agricultural residues that would otherwise be discarded or left to decompose, thus reducing waste generation and associated environmental impacts. - Providing a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels by utilizing biomass feedstocks, which are derived from renewable resources. - Promoting the use of by-products and co-products from biomass energy production, such as ash, biochar, and biogas digestate, for beneficial applications in agriculture, construction, and industry. - Enabling the integration of biomass energy with other sectors of the circular economy, such as sustainable agriculture, forestry, and waste management. 10. How can individuals contribute to the development of biomass energy? Individuals can contribute to the development of biomass energy by: - Supporting policies and initiatives that promote the adoption of renewable energy, including biomass, at local, regional, and national levels. - Educating themselves and others about the benefits of biomass energy and its role in sustainable development and climate change mitigation. - Exploring opportunities for utilizing biomass fuels, such as wood pellets or biofuels, in residential heating systems or vehicles. - Participating in community-based initiatives or cooperatives that promote the use of biomass energy and support local biomass projects. - Advocating for investment in research and development of biomass energy technologies to improve efficiency and reduce costs. - Making sustainable choices in daily life, such as reducing energy consumption, recycling organic waste, and supporting sustainable land use practices. 11. What are the potential future developments in biomass energy? Future developments in biomass energy include: - Advanced conversion technologies: Ongoing research aims to improve the efficiency of biomass conversion processes, such as gasification and pyrolysis, to enhance energy yields and reduce environmental impacts. - Sustainable biomass production: Efforts are being made to develop sustainable biomass production systems that minimize land use conflicts, preserve biodiversity, and ensure the long-term availability of biomass feedstocks. - Integration with other renewable energy sources: Biomass energy can be integrated with other renewables, such as wind and solar power, to provide a more reliable and balanced energy supply. - Bioenergy with carbon capture and storage (BECCS): Biomass energy combined with carbon capture and storage technology has the potential to achieve negative emissions, effectively removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. - Biofuels for transportation: Advances in biomass energy research aim to develop more efficient biofuel production processes that can replace fossil fuels in the transportation sector. 12. How does biomass energy compare to other renewable energy sources? Biomass energy has several advantages and disadvantages compared to other renewable energy sources: Advantages: - Energy storage: Biomass can be stored and utilized on-demand, unlike solar and wind energy, which are intermittent. - Baseload power: Biomass power plants can provide continuous baseload power, similar to fossil fuel power plants. - Resource availability: Biomass feedstocks are readily available in many regions, offering a reliable and locally sourced energy option. - Carbon neutrality: Biomass energy is considered carbon-neutral because the carbon dioxide emitted during combustion is offset by the carbon dioxide absorbed during biomass growth. Disadvantages: - Land use: Biomass cultivation may require significant land resources, potentially leading to conflicts with food production or natural ecosystems. - Emissions and air quality: Biomass combustion can release air pollutants, such as particulate matter and volatile organic compounds, which may have adverse effects on air quality and human health if not properly managed. - Resource limitations: The availability of biomass resources is limited by factors such as land availability, climate conditions, and sustainable management practices. - Efficiency and cost: Biomass energy conversion technologies may have lower efficiencies and higher costs compared to more mature renewable energy technologies like solar and wind power. In conclusion, biomass energy offers a renewable and sustainable alternative to fossil fuels, contributing to reduced greenhouse gas emissions, improved waste management, and energy security. The top 10 countries interested in biomass energy have demonstrated significant commitment and success in its utilization. However, challenges persist and further advancements in technology, resource management, and policy support are essential to fully harness the potential of biomass energy in the transition towards a greener future.