what are the uses of biomass energy
Best Uses of Biomass: A Green Renewable Bio-energy - Lets Do Garden
1. What is biomass energy and how is it produced?
According to experts, biomass energy refers to the use of organic materials, such as plants and animal waste, to produce heat, electricity, or other forms of energy. Biomass can be produced through various processes, including:
- Combustion: Burning organic materials to generate heat and electricity.
- Gasification: Converting organic materials into a gas through a high-temperature process.
- Anaerobic digestion: Decomposing organic materials in the absence of oxygen to produce biogas.
- Pyrolysis: Heating organic materials in the absence of oxygen to produce liquid or gas fuels.
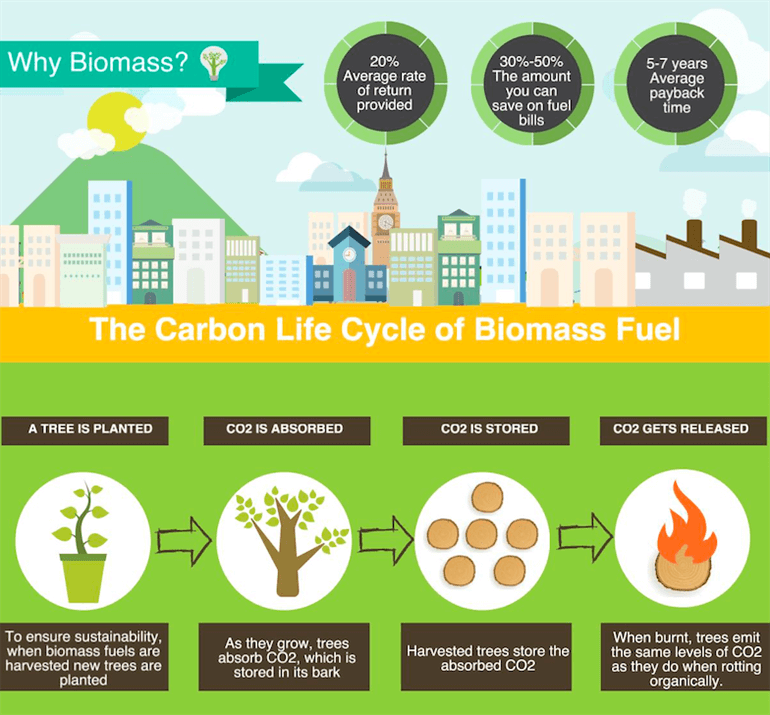
2. What are the benefits of using biomass energy?
Biomass energy offers several benefits, including:
- Renewability: Biomass is derived from organic materials that can be replenished over time.
- Reduced greenhouse gas emissions: Biomass combustion releases carbon dioxide, but it is offset by the carbon absorbed during the growth of the organic materials.
- Diversification of energy sources: Biomass provides an alternative to fossil fuels, reducing dependence on non-renewable resources.
- Waste management: Biomass can be derived from agricultural residues, food waste, and forestry byproducts, providing an effective way to manage and utilize organic waste.
3. Can biomass energy be used for residential purposes?
Yes, biomass energy can be used for residential purposes. Biomass boilers and stoves are available for home heating and cooking. These systems burn organic materials, such as wood pellets or logs, to generate heat. They are an eco-friendly alternative to traditional fossil fuel-based heating systems.
4. Is biomass energy more expensive than other forms of energy?
The cost of biomass energy varies depending on factors such as the type of biomass used, the scale of the project, and the availability of biomass resources. In some cases, biomass energy can be cost-competitive with other forms of energy, especially when there is a local abundance of biomass resources. However, it's important to consider the long-term benefits, such as environmental sustainability and energy security, when evaluating the cost-effectiveness of biomass energy.
5. Are there any limitations or challenges associated with biomass energy?
While biomass energy has numerous advantages, it also faces certain limitations and challenges, including:
- Feedstock availability: The availability and accessibility of biomass resources may vary depending on geographical location and seasonal factors.
- Infrastructure requirements: Biomass energy systems may require specific infrastructure, such as storage facilities and transportation networks, to efficiently utilize and distribute biomass resources.
- Emissions and air quality: The combustion of biomass can release pollutants into the atmosphere, requiring appropriate emissions controls and air quality monitoring.
- Competition with other land uses: Biomass production may compete with agricultural land and other land uses, raising concerns about food security and biodiversity.
6. How does biomass energy contribute to environmental sustainability?
Biomass energy contributes to environmental sustainability in several ways:
- Reduced carbon emissions: Although biomass combustion releases carbon dioxide, the absorption of carbon dioxide during the growth of organic materials offsets the emissions, resulting in a net-zero or even carbon-negative energy source.
- Waste utilization: Biomass energy allows for the efficient utilization of organic waste materials, reducing landfill waste and minimizing methane emissions.
- Promotion of circular economy: Biomass can be derived from agricultural and forestry byproducts, promoting a circular economy by utilizing materials that would otherwise go to waste.
- Renewable energy generation: Biomass is a renewable energy source, meaning it can be continuously replenished and does not deplete finite resources.
7. How does biomass energy compare to solar and wind energy?
Biomass energy, solar energy, and wind energy are all renewable forms of energy. However, they differ in terms of availability, scalability, and application:
- Solar energy: Solar energy harnesses the power of sunlight to generate electricity. It is abundant in most regions and can be deployed at various scales, from individual rooftop installations to utility-scale solar farms.
- Wind energy: Wind energy utilizes wind turbines to convert the kinetic energy of wind into electricity. It requires consistent wind resources and is often deployed in windy areas, such as coastal regions or open plains.
- Biomass energy: Biomass energy utilizes organic materials for heat, electricity, or fuel production. It can be produced locally and is suitable for both large-scale power generation and small-scale residential applications.
8. Can biomass energy help reduce dependence on fossil fuels?
Yes, biomass energy can help reduce dependence on fossil fuels. By utilizing organic materials, biomass energy provides a renewable and sustainable alternative to coal, oil, and natural gas. Biomass can be used to generate electricity, heat buildings, and even produce transportation fuels. By diversifying the energy mix, biomass energy contributes to energy security and mitigates the environmental impacts associated with fossil fuel consumption.
9. How does biomass energy support rural communities?
Biomass energy can have positive socio-economic impacts on rural communities:
- Job creation: Biomass energy projects, such as biomass power plants or pellet production facilities, create employment opportunities in rural areas.
- Local resource utilization: Biomass resources, such as agricultural residues and forestry byproducts, can be locally sourced, supporting the local economy and reducing dependence on external energy sources.
- Rural development: Biomass energy projects can stimulate rural development by attracting investment, providing revenue streams for farmers and landowners, and improving energy access in underserved areas.
10. Can biomass energy be used in vehicles?
Biomass energy can be converted into biofuels, which can be used as an alternative to gasoline and diesel in vehicles. Biofuels, such as ethanol and biodiesel, can be produced from various biomass feedstocks, including agricultural crops, algae, and waste oils. However, the widespread adoption of biomass-based biofuels in the transportation sector still faces challenges related to production scalability, cost-effectiveness, and infrastructure requirements.
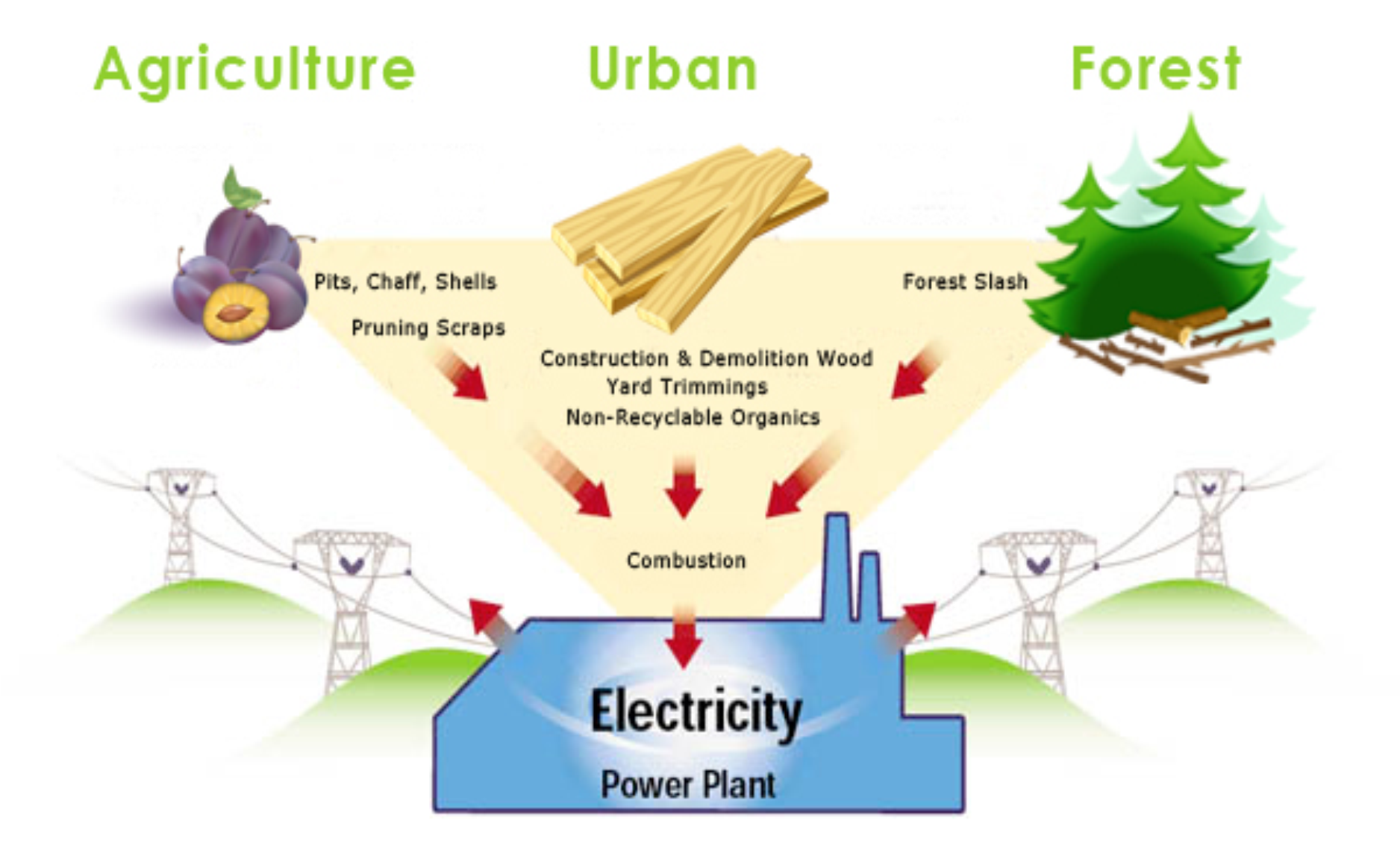
11. How does biomass energy contribute to waste management?
Biomass energy plays a crucial role in waste management by utilizing organic waste materials:
- Agricultural residues: Biomass energy can utilize crop residues, such as corn stalks or rice husks, that would otherwise go to waste after harvest.
- Forestry byproducts: Biomass energy can utilize wood chips, sawdust, and other waste materials from the forestry industry, reducing waste and promoting sustainable forest management.
- Food waste: Biomass energy facilities can process food waste, diverting it from landfills and reducing methane emissions.
12. How can individuals contribute to the development of biomass energy?
Individuals can play a role in supporting the development of biomass energy by:
- Adopting biomass heating systems: Switching to biomass boilers or stoves for residential heating can directly contribute to the demand for biomass energy.
- Supporting sustainable agriculture: Choosing sustainably produced biomass feedstocks, such as certified wood pellets or responsibly sourced agricultural residues, can promote the sustainable development of biomass energy.
- Advocating for renewable energy policies: Individuals can advocate for supportive policies and incentives that promote the growth of biomass energy, such as feed-in tariffs or renewable energy portfolio standards.
Reasons Why Biomass Energy Should Be a Top Choice - REURASIA
1. What is biomass energy and how does it work?
Biomass energy is a form of renewable energy derived from organic materials, such as plants and animal waste. It works by harnessing the energy stored in biomass through processes such as combustion, gasification, or anaerobic digestion. Biomass is burned or converted into a gas or liquid fuel to generate heat, electricity, or other forms of energy.
2. What are the advantages of using biomass energy?
When it comes to biomass energy, there are several advantages:
- Renewability: Biomass is derived from organic materials that can be regenerated over time, making it a sustainable energy source.
- Reduced greenhouse gas emissions: Biomass combustion releases carbon dioxide, but it is offset by the carbon absorbed during the growth of the organic materials, resulting in a net-zero or even carbon-negative energy source.
- Waste utilization: Biomass energy allows for the efficient utilization of organic waste materials, reducing landfill waste and minimizing methane emissions.
- Diversification of energy sources: Biomass provides an alternative to fossil fuels, reducing dependence on non-renewable resources and enhancing energy security.
3. Can biomass energy be used for large-scale power generation?
Yes, biomass energy can be used for large-scale power generation. Biomass power plants utilize organic materials, such as wood chips or agricultural residues, to produce electricity. These power plants can have a significant capacity and play a vital role in meeting the energy demands of communities or regions. Biomass power generation is a sustainable and reliable option for baseload power, providing a constant source of renewable energy.
4. Is biomass energy a cost-effective solution?
The cost-effectiveness of biomass energy depends on various factors, including the availability of biomass resources, the efficiency of conversion technologies, and the scale of the project. In some cases, biomass energy can be cost-competitive with other forms of energy, especially when there is a local abundance of biomass resources. However, economic viability should be assessed case by case, considering factors such as feedstock availability, technology costs, and potential revenue streams from byproducts such as heat or biochar.
5. Can biomass energy contribute to rural development?
Biomass energy can have positive implications for rural development:
- Job creation: Biomass energy projects, such as biomass power plants or pellet production facilities, create employment opportunities in rural areas, supporting local economies.
- Agricultural diversification: Biomass energy can provide additional revenue streams for farmers by utilizing agricultural residues or energy crops, enhancing agricultural diversification.
- Energy access in underserved areas: Biomass energy projects can improve energy access in remote or underserved rural areas, stimulating development and improving the quality of life for local communities.
6. Can biomass energy be used in industrial processes?
Yes, biomass energy can be used in various industrial processes. Industries such as pulp and paper, food processing, and manufacturing can utilize biomass as a source of heat or process energy. Biomass boilers or combined heat and power (CHP) systems can provide steam, hot water, or electricity for industrial operations, contributing to energy efficiency and environmental sustainability.
7. What types of biomass can be used for energy production?
A wide range of biomass feedstocks can be used for energy production:
- Wood: Wood chips, sawdust, and forestry residues are commonly used in biomass energy production due to their high energy content.
- Agricultural residues: Crop residues, such as corn stalks, rice husks, or sugarcane bagasse, can be utilized for energy production, reducing waste and enhancing agricultural sustainability.
- Energy crops: Dedicated energy crops, such as switchgrass or miscanthus, can be grown specifically for biomass energy production, providing additional revenue streams for farmers.
- Animal waste: Livestock waste, such as manure, can be anaerobically digested to produce biogas, a valuable source of renewable energy.
8. Is biomass energy environmentally friendly?
Biomass energy is considered environmentally friendly due to its renewable nature and potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. However, it is important to consider the overall lifecycle impacts of biomass energy, including feedstock production, processing, and transportation. Sustainable biomass sourcing, efficient conversion technologies, and appropriate emissions control measures are crucial for maximizing the environmental benefits of biomass energy.
9. Can biomass energy reduce reliance on imported energy sources?
Yes, biomass energy can help reduce reliance on imported energy sources. By utilizing locally available biomass feedstocks, biomass energy projects can enhance energy security and reduce dependence on fossil fuel imports. Biomass energy provides a domestic and renewable energy option, contributing to a more self-reliant and resilient energy system.
10. Can biomass energy be integrated with other renewable energy sources?
Yes, biomass energy can be integrated with other renewable energy sources to create a more diverse and resilient energy mix. For example, biomass power plants can be co-located with solar or wind farms, leveraging complementary characteristics to provide a stable and continuous supply of renewable electricity. Integrated systems can also optimize resource utilization and enhance overall system efficiency.
11. Are there any incentives or government programs to support biomass energy?
Many countries have implemented incentives or government programs to support biomass energy development, including:
- Feed-in tariffs: Governments may offer guaranteed electricity purchase prices for biomass-generated electricity, incentivizing the development of biomass power plants.
- Tax incentives: Tax credits or exemptions can be provided for biomass energy investments, reducing the financial burden and promoting private sector involvement.
- Renewable energy targets: Government targets for renewable energy deployment create a favorable policy environment for biomass energy projects.
- Research and development grants: Governments may provide grants or funding for research and development initiatives focused on biomass energy technologies or feedstock development.
12. What is the future outlook for biomass energy?
The future of biomass energy looks promising as the world seeks to transition towards more sustainable and renewable energy sources. Biomass energy technologies continue to improve, becoming more efficient and cost-effective. The development of advanced conversion processes, such as bio-refineries, can expand the range of products derived from biomass, including chemicals and bio-based materials. Biomass energy has the potential to play a significant role in decarbonizing the energy sector and achieving climate goals, while simultaneously supporting rural development and waste management initiatives.