Reasons Why Biomass Energy Should Be a Top Choice
1. What is biomass energy and how does it work?
Biomass energy refers to the energy generated from organic materials such as plants, crops, and wood. It can be produced through various processes like combustion, gasification, and anaerobic digestion. The organic materials are burned or converted into biogas to generate heat or electricity.
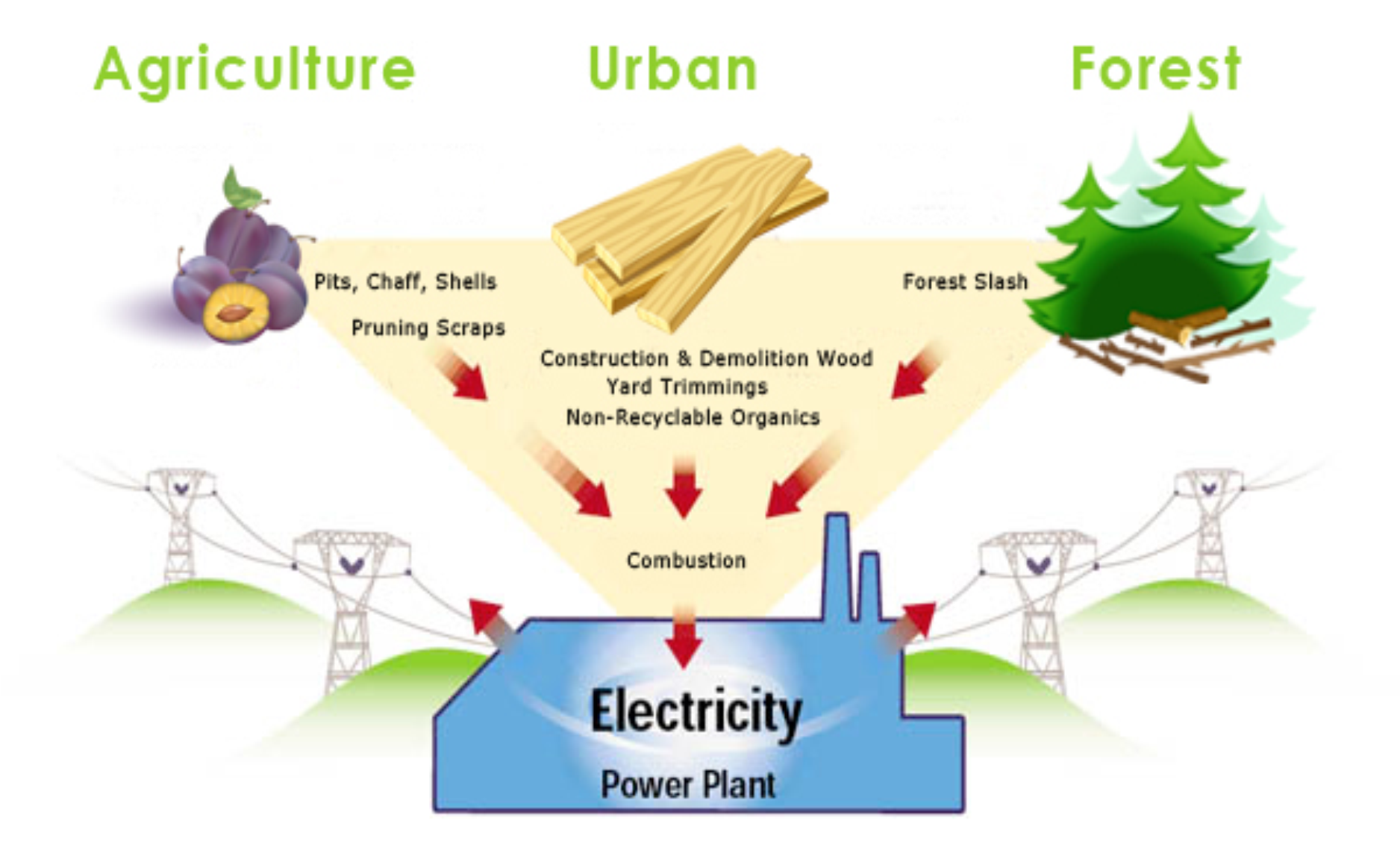
2. Is biomass energy a renewable energy source?
Yes, biomass energy is considered a renewable energy source because the organic materials used in its production are continuously replenished through natural processes like photosynthesis. This makes it a sustainable option for meeting energy needs while minimizing greenhouse gas emissions.

3. What are the advantages of using biomass energy?
- Biomass energy helps reduce the reliance on fossil fuels and contributes to a more sustainable energy mix. - It can help reduce waste and provide a way to manage organic materials that would otherwise end up in landfills. - Biomass energy production can create job opportunities in the renewable energy sector. - It can be produced locally, promoting energy independence and reducing dependence on imported fuels.
4. What are the potential environmental impacts of biomass energy?
- The combustion of biomass materials releases carbon dioxide, although it is considered carbon-neutral as the emitted CO2 is offset by the carbon absorbed during the growth of plants. - Other potential environmental impacts include air emissions, such as particulate matter and nitrogen oxides, which can be minimized through proper emission control systems. - The sourcing of biomass feedstock should be managed sustainably to prevent habitat destruction and biodiversity loss.
5. Is biomass energy cost-effective compared to other energy sources?
The cost-effectiveness of biomass energy varies depending on factors such as the availability and cost of biomass feedstock, technology used for conversion, and government incentives or subsidies. Biomass energy can be competitive in regions with abundant biomass resources and favorable policies supporting renewable energy.
6. How does biomass energy contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions?
Biomass energy is considered a low-carbon energy source because the carbon released during combustion is derived from recently absorbed CO2. This cycle is known as the carbon cycle, where new plant growth absorbs CO2, and when burned, releases it back into the atmosphere. Overall, biomass energy helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuel-based energy sources.
7. What are some examples of biomass feedstock?
- Agricultural residues like corn stalks, wheat straw, and rice husks - Wood pellets and sawdust from lumber and furniture industry waste - Energy crops such as switchgrass and miscanthus - Organic waste from food processing, animal manure, and wastewater treatment plants
8. Can biomass energy be used for heating purposes?
Yes, biomass energy is commonly used for heating purposes. Biomass boilers can burn wood logs, biomass pellets, or other forms of organic material to provide space heating and hot water for residential, commercial, and industrial applications.
9. Is biomass energy suitable for large-scale electricity generation?
Biomass energy can be utilized for large-scale electricity generation through dedicated biomass power plants. These facilities use advanced combustion or gasification technologies to convert biomass into heat or synthetic gases, which are then used to generate electricity through steam turbines or internal combustion engines.
10. What are the challenges in biomass energy production?
- Ensuring a sustainable supply of biomass feedstock without competing with food production or causing environmental damage - Developing cost-effective and efficient conversion technologies - Managing and minimizing air emissions and other environmental impacts - Overcoming the variability in biomass feedstock quality and composition
11. Can biomass energy be integrated with other renewable energy sources?
Yes, biomass energy can be integrated with other renewable energy sources to create a more balanced and reliable energy system. For example, biomass power plants can be combined with solar or wind energy facilities to provide a constant and stable electricity supply.
12. What is the future outlook for biomass energy?
The future of biomass energy looks promising as more countries strive to reduce their greenhouse gas emissions and transition to cleaner energy sources. Advancements in technology, improved biomass feedstock logistics, and supportive policies are expected to contribute to the growth of biomass energy in the coming years. By harnessing the power of biomass energy, we can take significant steps towards achieving a sustainable and environmentally friendly energy future. Alongside other renewable energy sources, biomass energy offers a reliable and carbon-neutral solution to meet our increasing energy demands.
