what is biomass energy definition
What is biomass energy: pro and cons, working and practical uses
Q1: What is biomass energy?
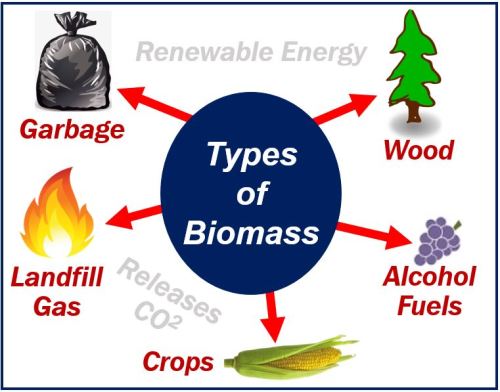
Biomass energy refers to the energy derived from organic materials, such as plants, wood, agricultural residues, and even municipal solid waste. It is a renewable source of energy as these organic materials can be replenished naturally. Biomass energy can be harnessed through various processes, including combustion, gasification, and anaerobic digestion.
Comprehensive structured answer:
- Biomass energy is derived from organic materials, providing a sustainable and renewable energy source.
- It can be obtained from a wide range of sources, including plants, wood, agricultural waste, and even garbage.
- Various processes can be used to convert biomass into energy, such as combustion, gasification, and anaerobic digestion.
- Biomass energy offers an alternative to fossil fuels and helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- It can be used for power generation, heating, and even transportation.
- Biomass energy has both advantages and disadvantages, which should be carefully considered in its implementation.
Q2: What are the pros and cons of biomass energy?
Comprehensive structured answer:
- Pros:
- Biomass energy is renewable and helps reduce dependence on fossil fuels.
- It reduces greenhouse gas emissions and contributes to combating climate change.
- Biomass resources are widely available and can be sourced locally, promoting energy independence and local economies.
- It can be used for various purposes, such as electricity generation, heating, and transportation.
- Biomass energy can be a sustainable solution for waste management by utilizing agricultural residues and organic waste.
- Cons:
- Biomass energy production can have environmental impacts, such as deforestation and habitat destruction if not managed sustainably.
- Certain biomass feedstocks may compete with food production or result in the diversion of agricultural land.
- Efficiency and energy content can vary depending on the biomass feedstock and conversion technology.
- Transportation and logistics of biomass materials can be challenging, especially over long distances.
- Some biomass conversion processes release pollutants and particulate matter, requiring proper emission controls.
Q3: How does biomass energy work?
Biomass energy can be harnessed through various processes:
- Combustion: Biomass materials, such as wood pellets or agricultural waste, are burned to produce heat, which can be used for heating spaces or generating steam to drive turbines for electricity generation.
- Gasification: Biomass is converted into a gas (syngas) by reacting it with high-temperature steam or oxygen. The syngas can be used for power generation or as a feedstock for producing biofuels.
- Anaerobic digestion: Organic waste, such as agricultural residues or food waste, is broken down by microorganisms in the absence of oxygen, producing biogas (methane and carbon dioxide). The biogas can be utilized for electricity generation or upgraded to biomethane for various applications.
Comprehensive structured answer:
- Several processes can be used to harness biomass energy, including combustion, gasification, and anaerobic digestion.
- Combustion involves burning biomass materials to produce heat or steam for electricity generation or heating purposes.
- Gasification converts biomass into a gas (syngas), which can be used for power generation or biofuel production.
- Anaerobic digestion breaks down organic waste using microorganisms, producing biogas that can be used for electricity generation or upgraded to biomethane for various applications.
Q4: What are the practical uses of biomass energy?
Biomass energy has various practical applications:
- Electricity generation: Biomass can be used to generate renewable electricity through processes like combustion or gasification.
- Heat production: Biomass can be burned or converted to heat, providing warmth for residential, commercial, or industrial heating purposes.
- Biofuels: Biomass can be processed to create biofuels, such as ethanol and biodiesel, which can be used as a substitute for fossil fuels in transportation.
- Cogeneration: Biomass power plants can produce both electricity and heat, allowing for efficient energy utilization.
- Bioproducts: Biomass can be used as a feedstock for the production of various bioproducts, including biochemicals, bioplastics, and biomaterials.
Comprehensive structured answer:
- Biomass energy has practical uses in electricity generation, heat production, biofuels, cogeneration, and the production of bioproducts.
- It can be a renewable source of electricity through combustion or gasification processes.
- Heat produced from biomass can be used for residential, commercial, or industrial heating purposes.
- Biofuels derived from biomass, such as ethanol and biodiesel, can serve as alternatives to fossil fuels in transportation.
- Cogeneration plants utilize biomass to produce both electricity and heat, maximizing energy efficiency.
- Biomass can also be used as a feedstock for the production of bioproducts, including biochemicals, bioplastics, and biomaterials.
Q5: How does biomass energy contribute to a sustainable future?
Comprehensive structured answer:
- Biomass energy offers several advantages in terms of sustainability:
- It is a renewable energy source as biomass materials can be replenished naturally.
- Biomass can reduce the dependence on finite fossil fuels and help mitigate climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Biomass resources are widely available locally, promoting energy independence and reducing transportation-related emissions.
- Utilizing biomass for energy purposes provides a sustainable solution for waste management by converting organic waste into valuable resources.
- Biomass energy can contribute to rural development and the creation of job opportunities in the agriculture and energy sectors.
- However, careful consideration of environmental and social factors is crucial for the sustainable implementation of biomass energy.
Q6: What are some examples of biomass materials?
Examples of biomass materials include:
- Wood and wood pellets
- Agricultural residues (e.g., corn stalks, rice husks, sugarcane bagasse)
- Energy crops (e.g., switchgrass, miscanthus)
- Algae
- Food waste
- Municipal solid waste
Comprehensive structured answer:
- Biomass materials can be diverse and include wood, agricultural residues, energy crops, algae, food waste, and municipal solid waste.
- Wood and wood pellets are commonly used biomass materials.
- Agricultural residues, such as corn stalks, rice husks, and sugarcane bagasse, can also be utilized.
- Energy crops like switchgrass and miscanthus are specifically grown for biomass energy production.
- Algae can be cultivated for biomass energy and other applications.
- Organic waste, including food waste and municipal solid waste, can also be valuable biomass resources.
Q7: How does biomass energy impact the environment?
Comprehensive structured answer:
- Biomass energy production can have both positive and negative environmental impacts:
- Positive impacts:
- Reduces greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuels, contributing to climate change mitigation.
- Provides renewable energy and promotes a shift away from non-renewable resources.
- Can serve as a sustainable solution for waste management by utilizing organic waste materials.
- Promotes the conservation of forests and natural resources by utilizing sustainably sourced biomass.
- Negative impacts:
- Deforestation and habitat destruction can occur if biomass feedstocks are not managed sustainably, leading to loss of biodiversity.
- Transportation and logistics of biomass materials can contribute to carbon emissions, especially when sourced from distant locations.
- Some biomass conversion processes may release pollutants and particulate matter, necessitating proper emission controls and monitoring.
- Land-use conflicts can arise when biomass feedstocks compete with food production or lead to the conversion of agricultural land.
Q8: How efficient is biomass energy?
The efficiency of biomass energy can vary depending on factors such as the biomass feedstock and the conversion technology used. However, it is generally considered less efficient compared to some other forms of renewable energy, such as wind or solar power.
Comprehensive structured answer:
- The efficiency of biomass energy can be influenced by:
- The moisture content and energy content of the biomass feedstock.
- The conversion technology used, such as combustion, gasification, or anaerobic digestion.
- The overall system design and efficiency of the power generation equipment.
- Efficiency can also depend on the scale and operational practices of the biomass facility.
- Biomass energy is generally considered less efficient compared to some other renewable energy sources, such as wind or solar power.
- However, biomass energy offers other unique advantages, such as its ability to provide baseload power and its utilization of locally available resources.
Q9: Can biomass energy replace fossil fuels?
Comprehensive structured answer:
- Biomass energy has the potential to replace fossil fuels in certain applications and contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- However, complete replacement of fossil fuels with biomass energy may not be feasible or desirable in all cases:
- Availability: The sustainable supply of biomass feedstocks may be limited in certain regions.
- Energy density: Biomass has lower energy density compared to fossil fuels, requiring larger volumes for the same energy output.
- Land use: Expanding biomass production may result in competition with food production or lead to the conversion of valuable ecosystems.
- Transition challenges: Existing infrastructure and systems are typically designed for fossil fuel use, making a complete transition to biomass energy challenging.
Q10: Is biomass energy renewable?
Comprehensive structured answer:
- Yes, biomass energy is considered renewable as the organic materials it is derived from can be naturally replenished.
- The growth of plants, trees, and crops used for biomass occurs through photosynthesis, utilizing sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide.
- By managing biomass resources sustainably and ensuring that the rate of consumption does not exceed the rate of regrowth, biomass energy can be renewable and help reduce reliance on non-renewable fossil fuels.
Q11: How is biomass energy different from other forms of renewable energy?
Comprehensive structured answer:
- Biomass energy differs from other forms of renewable energy, such as wind or solar power, in several ways:
- Source: Biomass energy is derived from organic materials, while wind and solar power harness natural forces (wind and sunlight) directly.
- Availability: Biomass resources are not dependent on weather conditions or geographical location, making them more consistent and reliable.
- Flexibility: Biomass can be stored and used on demand, providing a baseload power source that can also be dispatched when needed.
- Energy density: Biomass has lower energy density compared to some other renewable sources, meaning larger volumes are required for the same energy output.
- Environmental impact: Biomass energy production can have specific environmental considerations, such as land use impacts and emissions from certain conversion processes.
Q12: What are some success stories or case studies of biomass energy implementation?
Comprehensive structured answer:
- There are numerous successful examples of biomass energy implementation worldwide:
- Sweden: Sweden has achieved significant success in utilizing biomass for energy generation. Around 30% of the country's energy comes from biomass sources, including wood pellets, forest residues, and agricultural byproducts.
- Denmark: Denmark has implemented district heating systems that utilize biomass. These systems have helped reduce reliance on fossil fuels and decrease greenhouse gas emissions.
- United States: In the United States, biomass power plants have been established in various regions, utilizing agricultural waste, forest residues, and dedicated energy crops.
- India: India has made strides in utilizing biomass-based gasification systems for rural electrification, providing clean and sustainable energy to remote communities.
Overall, biomass energy offers a renewable and sustainable alternative to traditional fossil fuels. It has various practical uses, ranging from electricity generation to heat production and biofuel utilization. However, careful consideration of environmental and social factors is essential for its successful implementation. Biomass energy can contribute significantly to a sustainable future, but it should be integrated into a broader mix of renewable energy sources to achieve a diversified and resilient energy system.